Extended Trial Balance Business Definition
- What is trial Balance?
- Trial balance objective
- Features of trial balance
- Type of trial balance
- How to prepare a trial balance
- Trial balance example and format
- Forms of trial balance
- What accounts do we find in trial balance?
What is trial balance?
Trial Balance is a statement summarizing the closing balance of all the ledger accounts, prepared with the view to verify the arithmetical accuracy of ledger posting. In Trial balance, all the ledger balances are posted either on the debit side or credit side of the statement.
The total of debit balance in trial balance should match with a total of credit balance, only then it is said to be arithmetically accurate. Trial balance is a primary source for preparing various financial statements such as Trading and Profit & Loss account, Balance sheet etc.
Trial balance objective
As the name suggests, it's a statement prepared to ensure that journal and ledger postings are done correctly so that closing balances can be considered for preparing the final accounts and other financial statements. Trial Balance acts as a pre-check before preparing the other financial statements. The following are some of the important objectives of trial balance.
- To ascertain the arithmetical accuracy of ledger accounts:
As a summary of all the ledger accounts closing balance, trial balance helps in determining the accuracy of journal and ledger posting. The trial balance is assumed to be accurate only when the total debit is equal to the credit.
- Helps to locate errors
If there any difference in the trial balance, it signals that journal or ledger posting is not carried out efficiently. It clearly implies that there are errors and it is high time for accountants to find and correct it. The error may have occurred at any of the following stages of accounting.
- Posting journal entries to the ledger account
- Totaling of subsidiary books
- Calculation errors
- Posting of Balance from Ledger account to trial balance
- Error in totalling Trial balance and so on ...
- Helps to prepare financial statement
Trial balance is a bridge between accounting records and financial statements. Trial balance is the steppingstone for preparing all the financial statements such as Trading and Profit & loss account, balance sheet etc. Using the trial balance, all the income and expenses related ledger accounts are compiled to create Profit and loss account and rest are used for preparing a balance sheet.
Features of trial balance
- It is a summary of debit and credit balances which are extracted from various ledger accounts
- It is a summary of debit and credit balances
- The motive behind the preparation of Trial balance is to establish arithmetical accuracy of the transactions recorded in the Books of Accounts
- Trial balance does not prove any arithmetical accuracy of accounts which can only be determined by the audit
- It is not an account. It is only a statement of account
- It is not a part of the final statements
- A Trial balance at the end of the accounting year but it can also be prepared anytime as and when required like weekly, monthly, quarterly or half-yearly
- It acts as a bridge between books of accounts and the Profit and Loss Account and Balance sheet
Type of trial balance
There are different types of trial balance prepared at different stages of the accounting cycle. The following are different types of trial balance.
How to prepare a trial balance?
Preparing trial balance is one of the first steps towards preparing final accounts and other financial statements. Following are the steps to prepare trial balance:
- Preparing ledger accounts to determine the closing balance of each account.
- Post the ledger Accounts into trial balance and place the balance in the debit or credit column. The format of the trial balance is explained in the next section.
- All the assets and expenses should have debit balance while liabilities and income should have a credit balance.
- Calculate the total of the debit balance
- Similarly, compute the total of the credit column
- Finally, the sum of debit balance should match the sum of credit balance.
- If there is any difference, the process of error rectification should be started. Errors could be of commission errors, errors of omissions, errors of principle, compensating error and so on…
Trial balance example and format
To understand better, we have illustrated a sample trial balance format.
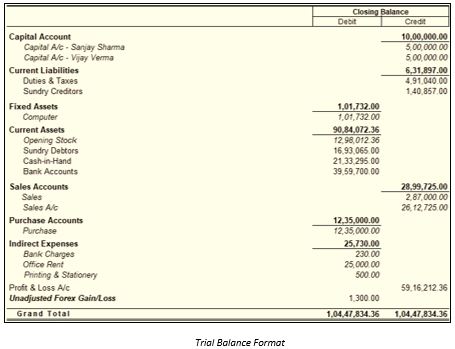
As illustrated in the above trial balance format, all the ledger accounts are represented on the left side. The closing balance of each ledger accounts is shown in the debit side or credit side in the above trial balance example.
Forms of trial balance
A trial balance could be prepared in two forms, as follows:
| Journal Form | This form of trial balance will have a format of journal folio. This includes a column for the serial number, name of the account, ledger folio, debit amount and credit amount columns in this journal form. The Ledger folio will show the page number on which such account appears in the ledger. |
| Ledger Form | This form of a trial balance will have two sides i.e. debit side and credit side. Here the ledger form of a trial balance is prepared in the form of an account. With each side of the trial balance having particulars such as (name of the account) column, folio column and the amount column. |
The trial balance must tally, irrespective of the form of a trial balance.
What accounts do we find in trial balance?
| Debit Side | Credit Side |
| All Assets ( Cash in hand, Cash at Bank, Inventory, Land and Building, Plant and Machinery etc. ) Sundry Debtors Expenses ( Carriage Inward, Freight, Rents, rebates and rates, Salary, Commission etc. ) Purchases Losses (Depreciation, Return inwards, Profit and loss A/c (Dr.), Bad debts etc. ) | All liabilities ( Bank Overdraft, Secured and unsecured loans, bills payable, Outstanding Payables or expenses, Loan on mortgage etc. ) Sundry Creditors Reserve fund, general reserve, provision for depreciation, Accumulated depreciation etc. Sales Gains ( Discount received, Return Outwards, Bad debts recovered, Profit and Loss (Cr.) etc. ) |
Trial balance relevance in modern day accounting
By now, we are clear that trial balance's primary objective is to ascertain the accuracy and detecting of errors. With the diversity of business operation and frequent need for financial statements, most of the businesses are using accounting software for managing the books and generating financial statements. Accounting software like TallyPrime, is designed to ensure that debit and credit always match at the time of recording the transaction itself. Thus, matching of the trial balance is a 'Thing of Past' and the traditional need for someone to depend on trial balance is eradicated.
Most businesses believe usingaccounting software gives a sense of reliability that once the transactions are recorded, the reporting aspect is correct and complete.
Read More on Trial Balance
How to Prepare Trial Balance, Methods to Prepare Trial Balance, Rules & Examples of Trial Balance, Errors in Trial Balance
Extended Trial Balance Business Definition
Source: https://tallysolutions.com/accounting/what-is-trial-balance/
0 Response to "Extended Trial Balance Business Definition"
Post a Comment